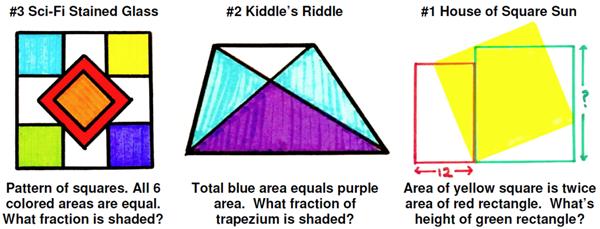
 I have been subverted again by a recent post by Ben Orlin, “Geometry Puzzles for a Winter’s Day,” which is another collection of Catriona Shearer’s geometric puzzles, this time her favorites for the month of November 2019 (which Orlin seems to have named himself). I often visit Orlin’s blog, “Math with Bad Drawings”, so it is hard to kick my addiction to Shearer’s puzzles if he keeps presenting collections. Her production volume is amazing, especially as she is able to maintain the quality that makes her problems so special.
I have been subverted again by a recent post by Ben Orlin, “Geometry Puzzles for a Winter’s Day,” which is another collection of Catriona Shearer’s geometric puzzles, this time her favorites for the month of November 2019 (which Orlin seems to have named himself). I often visit Orlin’s blog, “Math with Bad Drawings”, so it is hard to kick my addiction to Shearer’s puzzles if he keeps presenting collections. Her production volume is amazing, especially as she is able to maintain the quality that makes her problems so special.
The Stained Glass puzzle generated some discussion about needed constraints to ensure a solution. Essentially, it was agreed to make explicit that the drawing had vertical and horizontal symmetry in the shapes, that is, flipping it horizontally or vertically kept the same shapes, though some of the colors might be swapped.
See Geometric Puzzle Madness
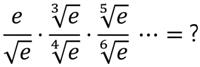 This is a delightful and surprising problem from Presh Talwalkar.
This is a delightful and surprising problem from Presh Talwalkar.
 Here is another train puzzle, this time from J. A. H. Hunter’s Entertaining Mathematical Teasers:
Here is another train puzzle, this time from J. A. H. Hunter’s Entertaining Mathematical Teasers: It is hard to believe a whole year has passed since I started this blog. What is even more surprising is that by February I thought I was about done. I had more or less uploaded the math curiosities and problems I had been thinking about over the years and had presented most of the math essays I had written. There are of course only a finite number of math problems in the world, so I thought I was about done. But much to my surprise I kept finding one more thing that interested me, either an essay or math problem. So here I am. We will have to see what the next year brings.
It is hard to believe a whole year has passed since I started this blog. What is even more surprising is that by February I thought I was about done. I had more or less uploaded the math curiosities and problems I had been thinking about over the years and had presented most of the math essays I had written. There are of course only a finite number of math problems in the world, so I thought I was about done. But much to my surprise I kept finding one more thing that interested me, either an essay or math problem. So here I am. We will have to see what the next year brings. I have been subverted again by a recent post by Ben Orlin, “
I have been subverted again by a recent post by Ben Orlin, “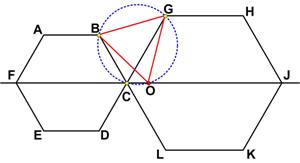 This is truly an amazing result from Five Hundred Mathematical Challenges.
This is truly an amazing result from Five Hundred Mathematical Challenges.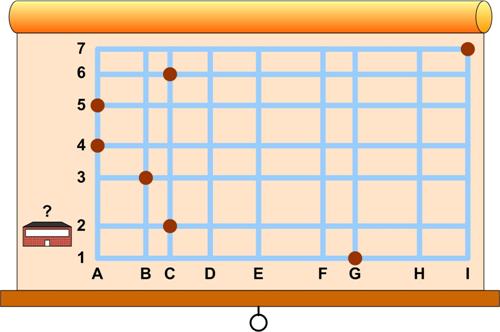 This is a somewhat elegant problem from the 1987 Discover magazine’s Brain Bogglers by Michael Stueben:
This is a somewhat elegant problem from the 1987 Discover magazine’s Brain Bogglers by Michael Stueben: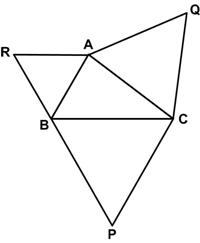 Here is another simple problem from Futility Closet.
Here is another simple problem from Futility Closet. If you will pardon the pun, this is a diabolical problem from the collection Five Hundred Mathematical Challenges.
If you will pardon the pun, this is a diabolical problem from the collection Five Hundred Mathematical Challenges. Here is another Brain Bogglers problem from 1987.
Here is another Brain Bogglers problem from 1987. For a number of years I have collected excerpts that portray mathematical ideas in a literary or philosophical setting. I had occasion to read a few of these on the last day of some math classes I was teaching, since there was no point in introducing a new subject before the final exam.
For a number of years I have collected excerpts that portray mathematical ideas in a literary or philosophical setting. I had occasion to read a few of these on the last day of some math classes I was teaching, since there was no point in introducing a new subject before the final exam.